Watch "Best Hair Transplant in Guwahati Assam" on YouTube
By PJMazumdar |2018-05-14 | General
Read MoreArogyam Hair Transplant & Cosmetic Clinic, Guwahati,Assam
8811077011 , 7637089211 guwahatihairtransplant@gmail.com
Dr. P. J. Mazumdar is the hair transplant doctor of Arogyam Hair Transplant clinic in Downtown Hospital, Guwahati, Assam. He is the pioneer FUE Hair Transplant specialist doctor of Guwahati, Assam and NE. Mastering from Guwahati Medical College, he is the first American Board Certified Diplomate in Hair Transplant from the American Board of Hair Restoration Surgery in North East India
and all procedures and counselling are performed strictly according to standard American and International ethical and technological guidelines.
Downtown Arogyam Hair Transplant Clinic performed the first FUE Hair Transplant in Guwahati, Assam in 2012.
and is the oldest and most popular HT clinic in Guwahati, Assam and the North East performing the highest number of surgeries per year in NE and strives to offer the most satisfactory hair transplant results in a completely modern and hospital based setting for total safety.

Cost in Reputed AHRS centers is calculated on the basis of the number of Follicular Units (FU) done.
A follicular unit is a collection of hair follicles - hair follicles do not exist singly but are grouped into clusters and these clusters are called follicular units or FU. Follicular Units are extracted and planted individually and each FU contains 1,2,3 or even more number of hairs.
Cost Depends on a Number of Factors

Downtown Hospital:
From 12PM to 4 PM
on all weekdays.
Arogyam Hair Clinic :
From 4 PM to 7 PM
on all weekdays.
Arogyam Hair Transplant Clinic is situated in Guwahati, Assam. It is a part of Downtown Hospital, Guwahati.
Dr. P. J. Mazumdar, MS, FICS, Diplomate ABHRS is the hair transplant doctor of Arogyam Hair Transplant clinic. All consultation and procedures are done by Dr. P. J. Mazumdar, Hair Transplant specialist. He is the only US Board Certified hair transplant doctor in the North East.
At Arogyam, the most modern hair transplant method, Blunt Motorised Blunt FUE, is used. This minimises hair injury thus allowing the healthiest and best growth of hair. This method was first introduced in 2006 by Dr. Sam Harris, the founder of modern FUE. Dr. P. J. Mazumdar trained under Dr. Sam Harris in 2016.
This is of course always an important consideration in cosmetic procedures.
Cost in Hair Transplant depends on the number of grafts to be done. The number of grafts needed in turn depends on the area that is empty and also on the desire of the patient. Patients having larger bald areas will require more grafts. Also the patient's desires like how much density he wants and the area he wants to cover all affect the price. Some centers nowadays quote a lump sum to patients or quote price in terms of square centimetres but this is not fully honest as the patient then does not know exactly what he or she is going to get. Also, quoting price in terms of hairs rather than grafts and offering discounts are other ways of confusing the patient. Although some centers nowadays quote a lump sum to the patient or in terms of square centimetres or in hairs instead of grafts, in all reputed AHRS accredited clinics cost is calculated in terms of grafts which ensures total honesty and transparency.
At Arogyam Hair Transplant Center we are committed to offering a straightforward honest appraisal for costs and also to keeping the costs at the lowest possible rate for the people of the Northeast.
Read more here about the costs of hair transplant Top 10 things you need to know about cost in hair transplant in Guwahati, Assam
Hair transplant is in general very safe procedure. Hair remains in the skin itself, and so the only thing that is dealt with in the procedure is the top layer of the skin. There is therefore little risk involved at all in any part of the procedure.
The main risks are: infection, allergic reaction to the medicines, hypotension and uneven results. All these risks can generally be avoided safely if done in a proper OT setting and hence it is important to check the status of the clinic before doing a procedure.
The FUE method is safer than the strip method. In the strip method, a strip of skin is cut out and the edges have to be sutured. Though even this method is very safe, yet there is slight risk of excessive bleeding, wound infection, nerve injury leading to long term pain, etc. In FUE, even these risks are minimized. A specialized small drill is used to remove the hair and special implanters are used to plant it back in the new site - risks involved in this procedure are relatively small.
In Hair Transplant, as in all medical procedures, it is extremely important to choose the right doctor and clinic. There are many new clinics mushrooming throughout India, and they all come with flashy advertising on the media and internet. A prospective patient is likely to get confused seeing the cheap discounts and catchy slogans that the companies come up with. What are the criteria that must be kept in mind so that a person can be sure that he is getting the right treatment and not being cheated? Look up here to understand what is important in selecting a doctor and clinic Top 30 Questions you need to ask for selecting your hair transplant doctor and clinic
You can get back to work from the very next day. That is the power of the Motorised Blunt FUE technique. It causes very little morbidity and the inconvenience is minimal. You may choose to wear a cap for about two weeks so that the signs of operation like a slight reddishness of the operated areas are not seen. After two weeks, even the cap is not necessary. There is minimal pain and swelling and in general this does not require absence from work.

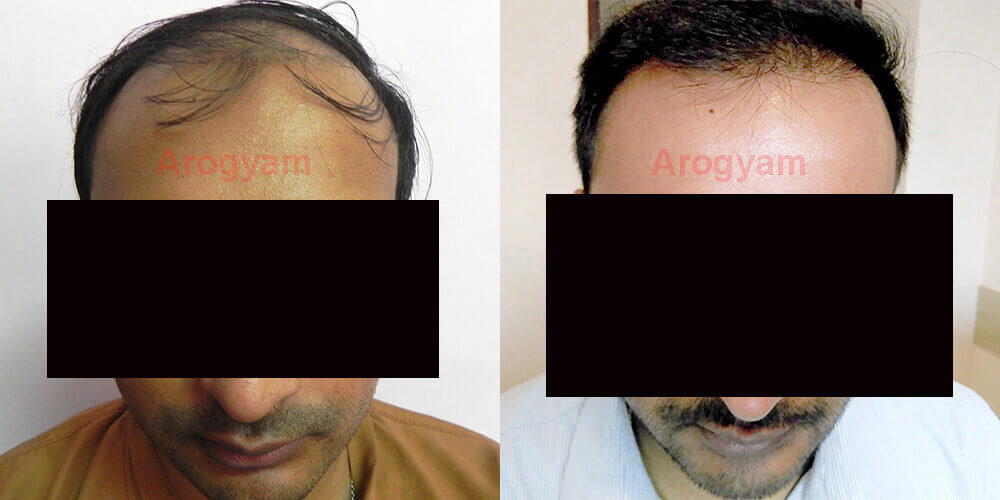
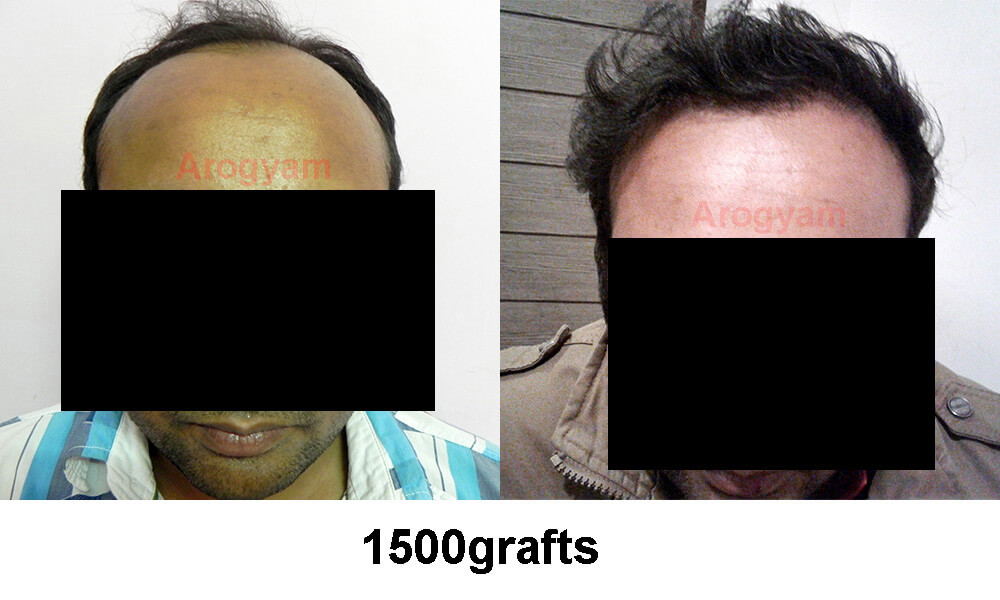
How do I select a good hair transplant clinic? What are the criteria for selection?
Hair transplant is a medical procedure which involves making incisions in the skin, both during extraction and planting. There are some important questions that the customer must ask both to ensure that he gets satisfactory results and for his own safety.
Hair transplant is a procedure for helping in hair loss
by transferring hair from the patient's own hair growing areas to bald areas. It is primarily used for male baldness but can also be used for female baldness, to reshape eyebrows, eyelashes, hair loss due to burns or trauma, etc
Hair transplant is a procedure used to treat areas of hair loss by transplanting hair from one site of the body to another.
It is primarily used in male pattern baldness, but is also used in female pattern baldness, loss of hair due to trauma, burns, surgical incisions, etc.
Male pattern baldness forms the bulk of the cases, upto 95%. Balding persons of all ages can get hair transplant done. Age range of hair transplant done in Arogyam Hair Transplant clinic ranges from 14 years (a young girl with burn injury of the scalp) to a 72 year old male.
Hair transplant is a cosmetic procedure. It is a purely elective procedure and personal aspirations of the patient are the main driving force for having this operation. Benefits from this procedure can be immense. Baldness can affect both social and professional life of the people who suffer from it, and people who are sensitive to it can become very self conscious about this and are unable to interact confidently with other persons. A hair transplant can be life changing in these situations.
Male pattern baldness or Androgenetic alopecia is controlled genetically. The hair follicles are genetically programmed to stop producing hair at a certain age which is determined by hereditary factors. These genes are activated by the effect of testosterone. Hair loss is graded according to the Norwood scale and graded from 1 to 7.During the balding process, the hair does not fall off directly, instead the hairs start getting thinner and shorter and do not reach their full length. In this way the density of hair covering the scalp is decreased. Hairs which fall off and are seen on the pillow and during showers are not due to balding.
The first recorded cases of hair transplant began in the early nineteenth century when some surgeons transplanted scalp flaps and free grafts to bald areas. Hair transplant was also done in Japan around 1930 when hair was transplanted to replace damaged eyebrows. Modern era of hair transplant began in late 1950’s when Dr. N. Orentreich transplanted free donor grafts to bald areas. He demonstrated that hair longevity was ‘donor dominant’, that is, the lifetime of a hair was determined by the site in which it grew originally and not the site to which it was transplanted. Dr. P. Walter defined the ‘Safe Donor Zone’ which contained hair with the maximum lifetime longevity.
Surgeons continued to develop techniques to transplant smaller and smaller grafts. Initially punch grafts were taken, but this gave an unnatural appearance to the new hair. In 1990, Limmer developed the technique of using microscopes to dissect follicular hair units from strips. Since then, the follicular unit has become the gold standard for transplantation. In 2002, FUE with extraction of single follicular units was developed. Initially manual punches were used but since 2004, motorized drills have come to be used in FUE and this is the most advanced technique at present.
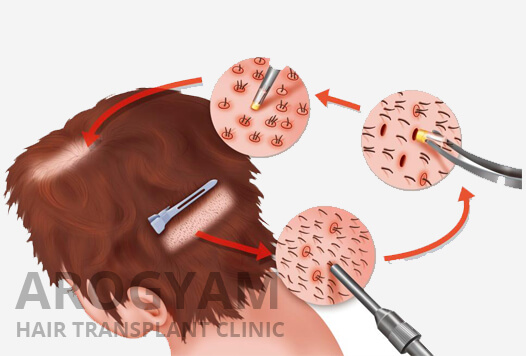
The concept of ‘Safe Donor Zone’ is the basis of hair transplant. It will be noticed that even in the most bald and elderly person, hair is still retained in the sides and back of the head. These are the areas in which hair is genetically programmed to last throughout life. This forms the catchment area for hair transplant. Hair is taken from this area and then transplanted to the bald areas. Hair is basically like a plant and the skin is like the soil. When a hair is taken out with its root from any area of the body and planted in the skin in a different part of the body, the hair will continue to grow in that area just like a plant which is removed from one field and planted in another.The transplanted hair lasts lifelong and this is what makes hair transplant so valuable.
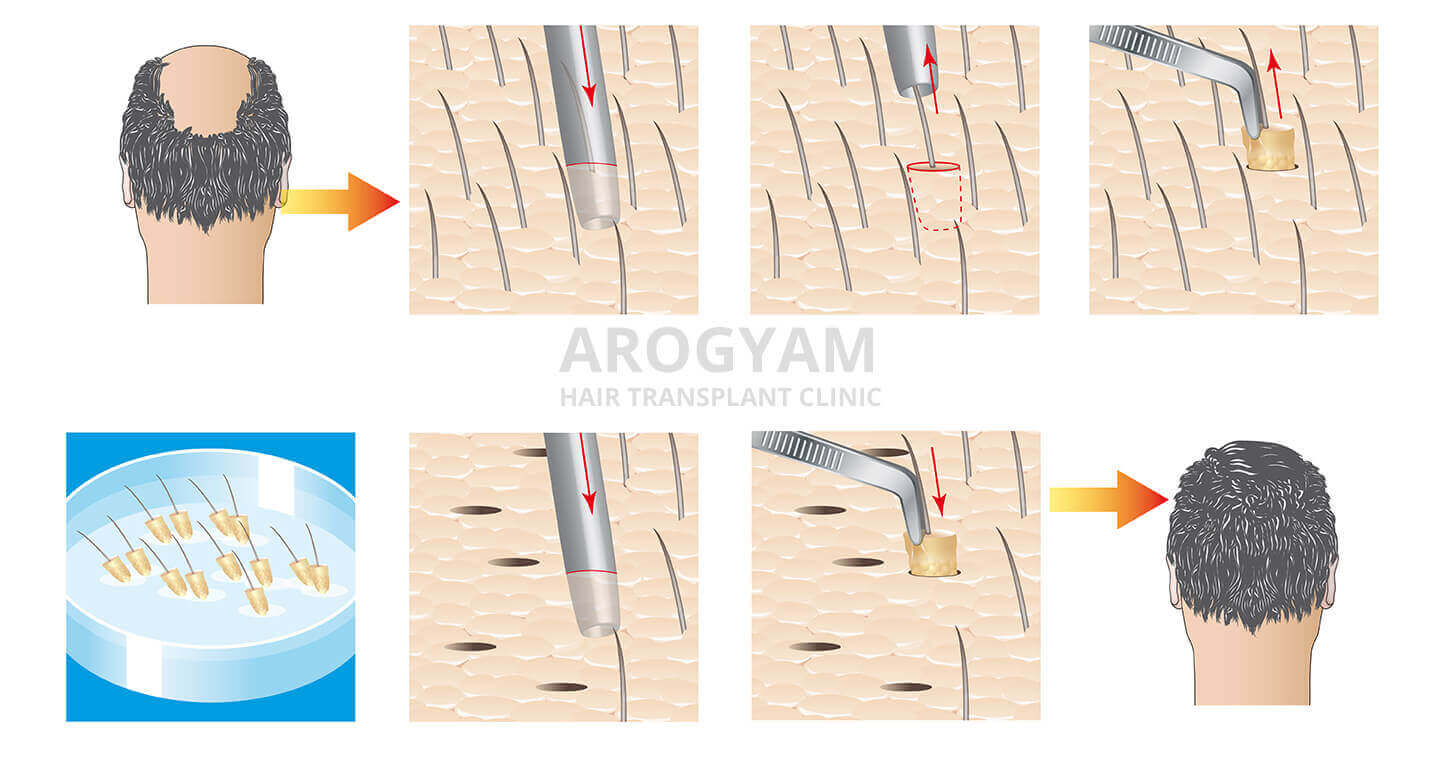
Hair transplant is done by two main methods, FUT and FUE. They differ only in the way hair is extracted, the plantation is done in the same way.
In FUT or Follicular Unit Transplantation or Strip Method, a strip of skin 1 cm wide is cut out from the occipital and temporal regions. Technicians then splice this strip into individual hair follicles. These follicles are then transplanted into the bald areas in the second stage.
In FUE, in the modern method, a drill of 1 mm size or smaller is used to carefully remove each individual hair follicle containing 1 to 4 hairs. Small round holes are left behind which form only minimal tiny round scars.. 1 out of 4 hair follicles are drilled out and the resulting slightly lower hair density is not noticeable at the donor site. The plantation method is the same.
The basic method of plantation is to create a small incision and then insert the hair follicle into it. The incision can be made with a small scalpel or a needle. Recently, customized transplanters like Choi implanters have been developed which makes the procedure faster and easier. Plantation is usually done by assistants.
Both the methods are done under Local Anesthesia. The patient remains fully conscious and injections are given in the skin to make the skin numb so that there is no pain during the procedure. FUE has the big advantage that it is much less painful postoperatively and it does not leave behind a scar.In FUT, the patient has a stitch at the back of the head which can cause discomfort for months even after the incision is healed, besides the scar. Maximum of 2000 grafts are done in a day. Usually a session on a single day will last about 6 hours but large sessions will last 8-9 hours. Breaks for lunch, toilet breaks, etc can be taken at any time without any problems. The patient can go home after the session and come again next day for the second session if needed. Typically FUE is more expensive than FUT because the surgeon has to spend more time.
Before the procedure, the patient has to be assessed psychologically. His needs are to be understood and the possibilities and limitations of the procedure explained. The patient needs to be explained that he should not expect a miracle like a complete return to his original hair pattern but only camouflaging by obtaining a natural hair line and increased hair density is to be expected. The amount of hair to be transplanted is decided based on factors like the amount of hair loss, costs, the expectations of the patient etc. Patients can go for a small transplant initially and then come back for further implants after 3 years or so as more of the original hair is lost.
For plantation, the surgeon has to decide the look of the hairline and then draw it out. The amount of hair planned to be transplanted, the age of the patient, the possibility of further loss of original hair, natural look, the density of hair planned, etc are all factors which need to be considered. Drawing of the hairline is more an art than science.
After the procedure is completed, the patient has a bandage at the back of the head but the transplanted area is kept free. Minimal precautions like avoiding rubbing the transplanted hair, etc are advised. Patient can wear a cap to cover the transplanted area from the next day. Shampooing of hair is advised after 4-7 days or earlier to wash out scabs.
Final results in hair transplant will take 6 to 9 months to show. After the transplant the hair will initially appear to be growing very nicely after 10 to 20 days. After that about half the hairs will fall. Only the outer portion of the hairs fall and the roots remain inside. This occurs because some of the hairs go into the telogen phase. At the end of one month about half the hairs will be growing and so only half the desired density will be visible. There will be no change for the next three months and it is common for patients to become anxious or depressed in this period. The roots of the hairs which have fallen off will start growing hairs again by the fourth month and the new hairs will start appearing. Almost all the fallen hairs will have appeared by 6 to 9 months and that is why full results should be expected only by 9 months. However, even after 9 months, for upto 1 and a half year, a few hairs will continue appearing and the existing hairs will also grow thicker and darker, and hence results will continue to improve till 1 and a half year.
Using FUE, surgeons are now able to use body hair also from the chest, back, arms and legs. Body hair is permanent but remains shorter in length. Using such hair, transplants upto 10,000 hairs have been done. But this is only for the very concerned patient who wants high density; for the average patient transplants of 1000 to 2000 hairs are usually satisfactory. This can be done in multiple sessions also over the years.
Hair transplant along with all other cosmetic procedures is growing in popularity in the present times. As people have more luxury and time to spare, no one wants to be left behind in the race for success and happiness. About 100,000 hair transplants were done in the US and about 280,000 worldwide in 2010. It is growing very fast in Asia since the last three years, and India also is showing a rapid growth. Not just male baldness but female hair loss and procedures for eyebrow and eyelash transplantation are also becoming increasingly popular. As with all cosmetic procedures it is a personal choice. For those who feel their baldness is a limitation, hair transplant has emerged as a safe and effective procedure with minimal side effects or drawbacks.
Arogyam Hair Transplant clinic has now been started in Downtown hospital to bring the advantages of this procedure to the people of the North-East. The latest FUE technique by motorized drill is used in the center. The aim is to provide the latest technology at an affordable cost and thereby benefit the people of this region. More than 500 patients have been operated till 2017 and many thousands more have been treated medically. The latest techniques and fully surgical safety is ensured to provide the best and safest results to the patient at a standardized cost.
What happens on the day of the procedure
Mesotherapy - Does it work?
It is primarily used in male pattern baldness, but is also used in female pattern baldness, loss of hair due to trauma, burns, surgical incisions, etc.
Male pattern baldness forms the bulk of the cases, upto 95%. Balding persons of all ages can get hair transplant done. Age range of hair transplant done in Arogyam Hair Transplant clinic ranges from 14 years (a young girl with burn injury of the scalp) to a 72 year old male.
Hair transplant is a cosmetic procedure. It is a purely elective procedure and personal aspirations of the patient are the main driving force for having this operation. Benefits from this procedure can be immense. Baldness can affect both social and professional life of the people who suffer from it, and people who are sensitive to it can become very self conscious about this and are unable to interact confidently with other persons. A hair transplant can be life changing in these situations.
Male pattern baldness or Androgenetic alopecia is controlled genetically. The hair follicles are genetically programmed to stop producing hair at a certain age which is determined by hereditary factors. These genes are activated by the effect of testosterone. Hair loss is graded according to the Norwood scale and graded from 1 to 7.During the balding process, the hair does not fall off directly, instead the hairs start getting thinner and shorter and do not reach their full length. In this way the density of hair covering the scalp is decreased. Hairs which fall off and are seen on the pillow and during showers are not due to balding.
The first recorded cases of hair transplant began in the early nineteenth century when some surgeons transplanted scalp flaps and free grafts to bald areas. Hair transplant was also done in Japan around 1930 when hair was transplanted to replace damaged eyebrows. Modern era of hair transplant began in late 1950’s when Dr. N. Orentreich transplanted free donor grafts to bald areas. He demonstrated that hair longevity was ‘donor dominant’, that is, the lifetime of a hair was determined by the site in which it grew originally and not the site to which it was transplanted. Dr. P. Walter defined the ‘Safe Donor Zone’ which contained hair with the maximum lifetime longevity.
Surgeons continued to develop techniques to transplant smaller and smaller grafts. Initially punch grafts were taken, but this gave an unnatural appearance to the new hair. In 1990, Limmer developed the technique of using microscopes to dissect follicular hair units from strips. Since then, the follicular unit has become the gold standard for transplantation. In 2002, FUE with extraction of single follicular units was developed. Initially manual punches were used but since 2004, motorized drills have come to be used in FUE and this is the most advanced technique at present.

The concept of ‘Safe Donor Zone’ is the basis of hair transplant. It will be noticed that even in the most bald and elderly person, hair is still retained in the sides and back of the head. These are the areas in which hair is genetically programmed to last throughout life. This forms the catchment area for hair transplant. Hair is taken from this area and then transplanted to the bald areas. Hair is basically like a plant and the skin is like the soil. When a hair is taken out with its root from any area of the body and planted in the skin in a different part of the body, the hair will continue to grow in that area just like a plant which is removed from one field and planted in another.The transplanted hair lasts lifelong and this is what makes hair transplant so valuable.
Hair transplant is done by two main methods, FUT and FUE. They differ only in the way hair is extracted, the plantation is done in the same way.
In FUT or Follicular Unit Transplantation or Strip Method, a strip of skin 1 cm wide is cut out from the occipital and temporal regions. Technicians then splice this strip into individual hair follicles. These follicles are then transplanted into the bald areas in the second stage.
In FUE, in the modern method, a drill of 1 mm size or smaller is used to carefully remove each individual hair follicle containing 1 to 4 hairs. Small round holes are left behind which form only minimal tiny round scars.. 1 out of 4 hair follicles are drilled out and the resulting slightly lower hair density is not noticeable at the donor site. The plantation method is the same.
The basic method of plantation is to create a small incision and then insert the hair follicle into it. The incision can be made with a small scalpel or a needle. Recently, customized transplanters like Choi implanters have been developed which makes the procedure faster and easier. Plantation is usually done by assistants.
Both the methods are done under Local Anesthesia. The patient remains fully conscious and injections are given in the skin to make the skin numb so that there is no pain during the procedure. FUE has the big advantage that it is much less painful postoperatively and it does not leave behind a scar.In FUT, the patient has a stitch at the back of the head which can cause discomfort for months even after the incision is healed, besides the scar. Maximum of 2000 grafts are done in a day. Usually a session on a single day will last about 6 hours but large sessions will last 8-9 hours. Breaks for lunch, toilet breaks, etc can be taken at any time without any problems. The patient can go home after the session and come again next day for the second session if needed. Typically FUE is more expensive than FUT because the surgeon has to spend more time.
Before the procedure, the patient has to be assessed psychologically. His needs are to be understood and the possibilities and limitations of the procedure explained. The patient needs to be explained that he should not expect a miracle like a complete return to his original hair pattern but only camouflaging by obtaining a natural hair line and increased hair density is to be expected. The amount of hair to be transplanted is decided based on factors like the amount of hair loss, costs, the expectations of the patient etc. Patients can go for a small transplant initially and then come back for further implants after 3 years or so as more of the original hair is lost.
For plantation, the surgeon has to decide the look of the hairline and then draw it out. The amount of hair planned to be transplanted, the age of the patient, the possibility of further loss of original hair, natural look, the density of hair planned, etc are all factors which need to be considered. Drawing of the hairline is more an art than science.
After the procedure is completed, the patient has a bandage at the back of the head but the transplanted area is kept free. Minimal precautions like avoiding rubbing the transplanted hair, etc are advised. Patient can wear a cap to cover the transplanted area from the next day. Shampooing of hair is advised after 4-7 days or earlier to wash out scabs.
Final results in hair transplant will take 6 to 9 months to show. After the transplant the hair will initially appear to be growing very nicely after 10 to 20 days. After that about half the hairs will fall. Only the outer portion of the hairs fall and the roots remain inside. This occurs because some of the hairs go into the telogen phase. At the end of one month about half the hairs will be growing and so only half the desired density will be visible. There will be no change for the next three months and it is common for patients to become anxious or depressed in this period. The roots of the hairs which have fallen off will start growing hairs again by the fourth month and the new hairs will start appearing. Almost all the fallen hairs will have appeared by 6 to 9 months and that is why full results should be expected only by 9 months. However, even after 9 months, for upto 1 and a half year, a few hairs will continue appearing and the existing hairs will also grow thicker and darker, and hence results will continue to improve till 1 and a half year.
Using FUE, surgeons are now able to use body hair also from the chest, back, arms and legs. Body hair is permanent but remains shorter in length. Using such hair, transplants upto 10,000 hairs have been done. But this is only for the very concerned patient who wants high density; for the average patient transplants of 1000 to 2000 hairs are usually satisfactory. This can be done in multiple sessions also over the years.
Hair transplant along with all other cosmetic procedures is growing in popularity in the present times. As people have more luxury and time to spare, no one wants to be left behind in the race for success and happiness. About 100,000 hair transplants were done in the US and about 280,000 worldwide in 2010. It is growing very fast in Asia since the last three years, and India also is showing a rapid growth. Not just male baldness but female hair loss and procedures for eyebrow and eyelash transplantation are also becoming increasingly popular. As with all cosmetic procedures it is a personal choice. For those who feel their baldness is a limitation, hair transplant has emerged as a safe and effective procedure with minimal side effects or drawbacks.
Arogyam Hair Transplant clinic has now been started in Downtown hospital to bring the advantages of this procedure to the people of the North-East. The latest FUE technique by motorized drill is used in the center. The aim is to provide the latest technology at an affordable cost and thereby benefit the people of this region. More than 500 patients have been operated till 2017 and many thousands more have been treated medically. The latest techniques and fully surgical safety is ensured to provide the best and safest results to the patient at a standardized cost.
Top 30 Questions You Need To Ask About Your Hair Transplant Doctor and Clinic in Guwahati Assam
All hair transplant customers in the region try to find the best hair transplant doctor and clinic in Guwahati, Assam and the Northeast. Hair transplant experts are doctors who are specialists in hair transplant surgery. Guwahati, Assam is the most popular destination for medical procedures like hair transplant and there are 5 hair transplant clinics in Guwahati itself out of which choosing the best can prove difficult for those who do not know the right things to ask.
Given here is a list of THE TOP 30 questions that YOU need to ask before choosing the best hair transplant doctor and clinic in Guwahati and the North East, 10 questions each about the Doctor, Clinic and the procedure itself.
10 questions to ask about your hair transplant doctor / specialist
10 questions to about your hair transplant clinic /hospital
10 questions to ask about your hair transplant procedure
10 questions about the hair transplant doctor/specialist in Guwahati
It is vital to know the qualifications of your doctor. Many unqualified persons like MBBS doctors, Ayurvedic or Homeopathic graduates and even techinicians can be found doing hair transplant in India and also in Guwahati. This is specially true of clinics which are branches of big chains of clinics and have roaming teams to do the transplant. Such clinics, and also some consultants, will gather all hair transplant patients till a number is reached and then call the team with which they have contact. These teams most often do not have qualified doctors - a qualified doctor does not need to go to patients, patients come to him. Such doctors are often anonymous and the consultant cannot even name them properly and may also give unverified 'degrees' which are dubious.
Dr. P. J. Mazumdar is the highest qualified doctor in the North East – he is the first and only US Board certified hair transplant specialist being a Diplomate of the American Board of Hair Transplant Surgery. This is the highest qualification in Hair transplant and there are only about 20 such qualified hair transplant specialists in India.
The experience of the doctor is the most important element in the success of hair transplant. In clinics with roaming teams of doctors/technicians, although the clinic chain as a whole may be experienced, no one can be really sure about the experience of the individual doctor/technician who is going to do the procedure. These roaming teams keep rotating their doctors /technicians bringing in new faces to cut cost
Dr. P. J. Mazumdar is the most experienced doctor in FUE Hair Transplant in the North East. He did the first FUE transplant in the North East in 2012 (the actual procedure of motorized FUE was invented only in 2006 in the US by Dr. Sam Harris). Since then, he has been performing the highest number of FUE surgeries in the North East each year and this number has been steadily growing.
In many clinics the person who does the initial consultation is not the operating surgeon and merely kept there to convince the patient with vivid descriptions but is unable to provide the actual information. The operating person sees the patient only just before the procedure. This is both dangerous and totally unsatisfactory, as the best results cannot be obtained in this way.
In Arogyam Clinic, Dr. P. J. Mazumdar himself will examine the patient right from the first consultation to the end of the procedure ensuring that the patient is well informed about all the steps of the procedure.
In many clinics, the doctor does not do all the steps of the procedure. He may do only the initial hairline or a few extractions leaving the rest of the procedure to the technicians. This is dangerous and illegal.
In Arogyam Hair Transplant Clinic, Dr. P. J. Mazumdar himself will do all the steps of the procedure from initial consultation to hair line drawing to follicular unit extraction to slit making, as per the norms of the AHRS and ABHRS.
In clinics with roving teams of doctors / technicians, the person doing the aftercare is different from the persons who did the procedure. This is an unsound practise and can lead to problems for the patients.
In Arogyam Clinic, Dr. P. J. Mazumdar will always be available for aftercare himself.
In case of chain clinics and some consultants who bring in operating teams from outside, once the operating person has completed the case, he leaves the state itself and goes back to his hometown. The patient cannot locate his operating doctor any more and has to depend on advise from someone who does not know how the procedure is actually done. Take care to ask if the operating doctor will be available for post operative queries.
Dr. P. J. Mazumdar will be stationed in Downtown hospital and is always available for all queries of the patient in the post operative period, which is very important for the patient.
Today there are many different types of people doing hair transplant even in Guwahati. Many persons are quite ready to cheat patients using the patient's lack of knowledge of technicalities. The commonest method is to quote 'follicular units' for 'hairs'. One follicular unit contains 2.5 hairs on the average, and price should ethically be quoted in terms of FU (follicular units), but many clinics will count hairs as FU. Clinics also do not give any option to the patients to verify the number of FU received, and give much less than the promised number. Also unrealistic boasts like '5000 FU in one day' are common for such clinics. Prospective hair transplant customers should be aware of these false claims. The highest number of FU that can be done in a day as per International norms is generally 2500 FU, and that too is a high figure.
Dr. P. J. Mazumdar, being a Diplomate of the American Board of Hair Transplant Surgery, and also a member of the Ethics Committee of the Association of Hair Transplant Surgeons of India, is duty bound to follow all ethical guidelines and customers can be assured that they will receive true facts at Arogyam.
Hair transplant is a rapidly advancing field and many new developments are taking place in this field. It is necessary to remain upgraded with the latest knowledge to take advantage of these developments. Professional money minded clinics generally will not invest in new technologies in order to maximise their profits.
Arogyam Clinic updates its procedures regulary and Dr. P. J. Mazumdar is a regular at all national and International conferences in order to acquire the latest instruments, technology and knowledge to achieve the best results in hair transplant.
Clinics relying on fly by night doctors are unable to give a full account of the qualifications of their doctors, and such doctors are often unqualified and untrained, and sometimes there are even technicians masquerading as doctors. Membership of professional bodies is a tool to ensure that your doctor is fully qualified and all potential customers must make this quer.
Dr. P. J. Mazumdar is a Diplomate of the American Board of Hair Restoration Surgery which is the highest body of hair transplant surgeons throughout the world. He is also a member of the Association of Hair Restoration Surgeons of India and is member of the the Ethics Committee of the AHRSI.
Besides qualifications, it is important to know where a doctor has been trained. Most clinics with roving doctors are unable to give this information as the doctor or technician has not received adequate training.
Dr. P. J. Mazumdar received his initial training under Dr. Vasa and since then has attended numerous workshops where he has been trained under the best International and National experts like Dr. Sam Harris, the inventor of the modern method of FUE, the motorised FUE, Dr. Farjo, Dr. Besham and many others.
10 questions about the hair transplant clinic in Guwahati
Most hair transplant clinics in Guwahati at present operate from small rented establishments which are not at all fit to be operating rooms. A medical establishment with operating rooms where surgical procedures are going to be done has a huge number of requirements and cannot just be set up by renting a few rooms. Hence it is very important to ensure whether all the norms have been met, which is virtually impossible in a rented extablishment, often with many other shops, restaurants and bars nearby.
Arogyam Hair Transplat Clinic performs all its procedures in Downtown Hospital, the largest private hospital in the North East, and the procedures are done in the Main OT Complex of Downtown Hospital, thus ensuring that patients are assured of receiving the best of care.
It is also important to enquire whether the clinic is a well reputed and established one. Many clinics are set up as fly by night projects which have no prior reputation and are set up mainly to make profits.
Arogyam Hair Transplant Clinic and Downtown Hospitals are both well established Institutions which have a long list of achievements to their credit and enjoy a strong and well earned reputation as the best in their field.
It is also important to ask how much experience the clinic has in hair transplant. Although the chain clinics may have experience overall, the particular branch at Guwahati will have done only a few procedures till date. The overall experience of the clinic chain cannot compensate for the lack of experience of the clinic as it is the experience of the staff, etc which will count in the success of the procedures and also in any emergencies.
Arogyam Hair Transplant Clinic has the highest experience in FUE Hair Transplant, performing the first FUE hair transplant in the region in 2012, only a few years after motorised FUE was started in the US in 2006. Since then, it has been the most popular FUE clinic in the North East performing the highest number of procedures in a year and this number has been growing steadily over the years.
This is an important question to ask as small rented establishments cannot fulfil all the norms that are required of an OT before a surgical procedure can be done there. An inadequate OT exposes the patient to several risks and also acts as limitations to the success of the procedure.
Arogyam Hair transplant clinic performs its procedures in the Main OT Complex of Downtown Hospital which is built according to all the latest norms and standards required of an Operating Room and ensures full safety of the patient and helps to reach the greatest success of the procedures.
This is a crucial question to ask about the hair transplant clinic. Proper emergency backup is a must to ensure safety of the patient. Although hair transplant is considered a very safe procedure, it is still ultimately a surgical procedure and risks can occur because of untoward reactions of the patients to drugs used during the procedure. This can be easily tackled when the clinic has the required emergency equipment and backup, but if these are lacking the patient can be in serious danger.
No other clinic in the North East can claim the emergency backup of Arogyam Clinic. All procedures take place in the Main OT of Downtown Hospital with its full array of Emergency backup including Emergency Anesthesiologists and all necessary equipment, staff specially trained in Emergencies, and even ICU nearby if necessary. All other clinics in the North East are stand alone clinics in rented rooms with no emergency backup.
Proper sterilisation is a must for all procedures. Sterilization requires a umber of important steps which must be performed correctly, such as autoclaving of instruments and clothes, liquid disinfectants for sharp instruments, regular fogging of the OT room, use of disposable equipments, etc. Such procedures are difficult to ensure correct performance and small stand alone clinics are likely to have gaps in their sterilization procedures.
Downtown OT complex has all the necessary equipment and procedures to ensure full sterilisation of each and every case. All procedures of Arogyam Hair Clinic are performed in Downtown OT.
Success of hair transplant requires that the best and most modern instruments are used for the transplant. This ensures optimal results of the procedure. It is important to enquire whether the clinic is using the latest technology.
Arogyam Hair Transplant clinic can justifiably claim to be using the latest technology in the field of hair transplant from 6X Heinz loupe, Blunt Titanium punches, Choi Implanters, Graft counters, etc.
It is important that all staff should be fully trained and qualified. Even a single under qualified nurse or staff can be the weakest link in the chain and can cause the whole procedure to fail by not doing his or her work properly. Most clinics use a number of staff who are not qualified and have no theoretical knowledge and learn their work at the clinic itself by observation.
All staff in Arogyam clinic are fully qualified staff nurses who are trained in emergency procedures.
There are a number of legal requirements for maintaining a medical clinic and full documentation is a must for all procedures. This is necessary for ensuring the safety of the patient and for standardisation of procedures.
Arogyam Hair Transplant Clinic along with Downtown Hospitals maintains all records and documentation and meets all legal requirements according to ISO 2002 standards. This ensures the highest level of standardisation. All taxes including GST are paid in full and strict documentation of all cases is ensured, and complete patient confidentiality is maintained.
Supporting facilities like pathology lab, Blood Bank, ICU, etc ensure full safety and backup for the patients. Stand alone clinics do not have any of these facilities and would require the patient or attendants to run around for simple requirements, and this can be a disaster during emergencies.
Arogyam along with Downtown hospitals have all these facilities thus ensuring a safe and convenient procedure for the patient.
10 questions about the hair transplant procedure
Hair Transplant in fact is not the only procedure for all bald patients. There are many cases of baldness where in fact hair transplant is not recommended, like unpatterned hair loss, alopecia universalis, etc. Hair transplant is to be avoided in such cases. Also in cases of young patients presenting with minimal loss, it is often better in the patients interest to delay the transplant. There are many other cases where the best procedure is not hair transplant but medicines or other forms of treatment. Advisers in small clinics do not have all the knowledge to determine when hair transplant is not the answer, and they are also driven by greed to suggest the highest number of follicular units that the patient can bear in all cases.
Arogyam Hair Transplant clinic follows all ethical guidelines of the American Board of Hair Restoration Surgeons and only the best and most appropriate advise is given to the patient. Patients who do not require surgery are prescribed other forms of treatment like medicines, hair patches, etc. Also only the most appropriate number of follicular units are advised and all factors are considered in determining this number.
It is very important to understand that baldness can be a continuous process. A person who now shows baldness at the back only can soon start showing baldness at the front also. This is specially so in case of young persons whose baldness is at the initial stages. Hence proper counselling is a must for all balding patients to ensure that care is taken of the future needs of the patient also. This requires a genuine desire to see that the patient is benefitted in the long term also and not just do a maximal transplant in the first stage without caring what will happen to the patient some years later.
At Arogyam Hair Transplant clinic, care is taken in counselling the patient to ensure that they understand the nature of their hair loss so that only the best possible advise is given which will take care of the long term needs of the patient also.
Hair transplant is not the only treatment for baldness. Many other treatments like medical treatment and also Hair Pieces (artificial hair) can be given for baldness. Transplant is required in many cases but not in all. It is important to know all the choices available before making a decision.
It is very important to know the survival rate of transplanted follicular units. Many clinics claim total or close to total FU survival to impress potential customers, but this is a false claim.
Internationally 85 to 95% survival rate is considered very good. Arogyam consistently achieves survival rate of around 92%.
It is also important to ask this question. Internationally a good clinic does between 2000 to 2500 follicular units in a day. This ensures optimal results. Some clinics even in Guwahati claim they can do upto 5000 follicular units a day, this is a false claim as it is simply not possible to do this number of FU in one day. Such claims prove that the clinic is cheating either by giving lesser number of FU than they show or counting hairs as FU..
This is the step where patients are typically cheated in most clinics. No clinic has proper verification methods of the number of FU that they do. The patient is then left at the mercy of the clinic hoping that they have fulfilled their promises. But most, if not all, clinics cheat on this score and give lesser number of FU than promised. Sometimes clinics ask the patients or attendants to count the FU but this also is not a sure method as no one can possibly manually count all the FU within the short time at their disposal.
At Arogyam, a special verification method is used so that no patient has any doubt in his or her mind. Follicular Units are placed in special counting trays and patients are asked to take pictures of these trays which they can then then zoom in and count later if they wish. This ensures that no patient has any doubt in his or her mind about the number of FU that were actually done.Not just the number but the quality of the ollicular Units, whether they have been transected or are whole, the number of hairs per FU, etc can all be checked so that the patient is fully confident in what was done..
Is the counting done by follicular units or hairs? How can I verify thi?
Difference between follicular units and hairs is another way in which clinics will typically cheat their patients. A FU contains between 2 to 3 hairs on the average and ethically counting and pricing should always be done in terms of FU and not hairs. But many unethical clinics will count hairs as FU and thus cheat their patients, who have no way of verifying whether hairs or FU were counted.
At Arogyam, pictures are given to patients of the counting trays and this can be used to verify that indeed FU were used and not hairs.
A well planned hair transplant requires that the density of hairs at different sites of the scalp is also planned beforehand and the implantation is done following this density. Thus for a successful result the correct density must be determined beforehand. The patient has a right to know what density has been planned for him and the doctor must be able to explain this. Hence it is important to ask this question beforehand, however many clinics do not have proper planning and cannot give this information.
At Arogyam, not only is the density planned but to ensure correct density, density stamps are used so that the density is given with precision.
International research has continuously led to improved techniques and guidelines which ensure optimal results. It is important that this latest knowledge is used in the clinic and correct operational procedures are followed.
Arogyam Hair Transplant clinic follows all the latest technical guidelines and procedures as advised by the American Board of Hair Transplant Surgeons and ensures the best results for the patients.
Post operative care and medicines required should be ascertained before the transplant. Long term medicines are not needed after the transplant but sometimes medicines may be prescribed for existing hair in order to preserve existing hair.
Top 10 things you need to know about cost in hair transplant in Guwahati, Assam and the North East
Cost in hair transplant varies widely in different regions, and different people will be quoted different costs even in Guwahati itself. You definitely want the best results for your transplant, and it may be confusing to understand why different costs have been quoted for the same person. Cost in hair transplant depends on three main factors – the degree of baldness of the patient, the expectation of the patient and the rates of the clinic. Besides this, there are a number of other factors which influence cost in hair transplant in Guwahati. Because of the wide variation in costs that are quoted to the patient, you need to understand the factors which influence the costs, and also the right questions to ask so that you get the best results for your money. Here the top 10 things you need to understand about cost in hair transplant in Guwahati, Assam and the North East.
Dr. P. J. Mazumdar is the most qualified hair transplant specialist in the North East as he is the only Diplomate in Hair Transplant Surgery from the American Board of Hair Transplant Surgeons. He is also the most experienced as he started FUE Hair Transplant in Guwahati and the North East in 2012, and performs by far the highest number of FUE procedures per year in the North East.
Downtown hospital is the largest private hospital in the North East and Arogyam Hair Transplant Clinic is the only clinic in the North East to be situated in a hospital. All other clinics in the North East operate from rented premises with their inherent disadvantages. Full safety and sterility is ensured as the procedure is done in the fully equipped Main OT of Downtown hospital.
At Arogyam, strict ethical standards are maintained and all costs are quoted in grafts, which is the internationally accepted norm. Also, full verification is given to the patient by using counting trays in which the grafts are placed and then giving photos of these trays to the patients on their mobile, so that they can later zoom in and see whether grafts or hairs are being used and also count them easily on the counting trays. Thus no room is left for doubt in the mind of the patient.
At Arogyam, we use the most advanced technique, Blunt Motorised FUE, and the best instrumentation like 6X Heinz loupe, Choi Implanters, Blunt Titanium punch, density stamps, counting trays, etc to ensure the best results for the patient.
Full Emergency services are possible only in a hospital setting and at Downtown hospital, we have the entire range of Emergency services to ensure full support in case of any emergency.
Downtown hospital has all the necessary infrastructure to support any big surgery including open heart surgery, kidney transplant, brain surgeries, etc and hence you will be assured of full support.
Downtown of course ensures that all such documentation is maintained up to the highest standards.
Costs in Arogyam Hair Transplant Clinic are maintained according to the standards we provide. We are not the cheapest clinic in Guwahati or the North East, but we are not the most expensive either, our prices are in the middle range. But we can justifiably claim that we provide the best treatment according to all International ethical and technical standards and we do not compromise on quality.
Our price is Rs 35 per graft plus GST. This is in the middle range of prices in India and also in Guwahati for any Association of Hair Restoration Surgery registered clinic and doctor.
For a Grade 3 baldness, cost would be around Rs 30,000, for Grade 4 around Rs 40,000 to Rs 60,000 , Grade 5 between Rs 60,000 to Rs 80,000, Grade 6 Rs 1 lakh to Rs 1.2 lakh and Grade 7 more than Rs.1.5 lakhs. This is if they want to cover the whole scalp with high density, but as explained before you can also choose to do a lesser number of grafts and thus your cost can be lower than this also.
There are at present 5 Hair transplant Clinics in Guwahati. Yes, there are 5 now! When we started we were the only clinic doing FUE Hair Transplant back in 2012. They are, in alphabetical order:
Arogyam Hair Transplant Clinic, Downtown hospital -owned by Dr. P. J. Mazumdar, MS, FICS, ABHRS Diplomate
Dr. Paul, Zoo Tiniali – part of a chain which started as a homeopathy clinic for hair.
DHI, Supermarket police point – part of a chain of clinics
HHY, Bhangagarh – part of a chain of clinics
Monjoven, VIP Road – owned by Dr. Porag Neog, MS. First hair transplant in the North East was done in Monjoven using strip method in 2010.
Prices, according to telephonic quotations, are:
Arogyam: Rs 35 per graft
Dr. Paul: Rs. 25 per graft
DHI: Rs. 65 per graft
HHY: Rs. 30 per graft
Monjoven: Rs 35 per graft
As you can see, we fall in the middle range of prices.
Each clinic has its own strength and weaknesses. Different patients choose different clinics as per their priorities. As a prospective customer, you should examine each clinic and determine which would suit you best.
Our disadvantages are:
Our advantages are:
Read up more here:
About Dr. P. J. Mazumdar and Arogyam Hair Transplant Clinic
Top 30 questions you need to ask about your Hair Transplant Doctor and Clinic
Know more about the American Board of Hair Restoration Surgery
PRP in Guwahati Assam - Role of PRP in hair fall and hair weakness
PRP or platelet rich plasma is a form of treatment using the patient's own blood which is becoming increasingly popular in recent times in treating a variety of conditions including hair loss.
Platelets are a type of cells found in the blood of humans whose primary function is in clotting of blood. Platelets also contain a large number of growth factors which help in the stimulation of the healing process and it is these growth factors which are most useful for treatment of various conditions.
PRP is produced from blood. About 10 ml of blood is collected from the patient and this blood is then treated with some reagents and then centrifuged through a special double centrifuge method till a small volume, approx.. 1 ml of PRP is produced. The processing ensures that this small concentrated plasma is very rich in platelets. This is the PRP solution. This solution is then injected into the area to be treated so that the platelets release their growth factors at the site and cause healing.
PRP has become most famous for being used by various highest level athletes like Tiger Woods and Rafael Nadal in treatment of injuries. PRP injected into muscular and tendon injury sites speed up the healing process significantly and is thus used for healing. It is also used in various orthopaedic lesions like Osteoarthritis where it brings about healing.
PRP is also increasingly being used in hair loss lesions like Alopecia areata and also in Androgenetic alopecia or Male Pattern baldness.
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where a small round lesion develops due to an autoimmune process. PRP injected into such lesions help significantly in promoting healing up of these lesions.
PRP is also increasingly being used in the most common type of hair loss, Male Pattern Baldness or Androgenetic alopecia. Although there were mixed results initially, various studies have now confirmed that PRP does work and gives good results in male pattern baldness. It is most effective in decreasing hair loss and has a minimal effect in growing new hair. In cases of progressive hair loss it helps to stop further increase in baldness. In cases of high hair fall and thinness/weakness of hair, it helps to stop further hair fall and also increases hair thickness and tensile strength. It is thus very useful for those who are having hair fall with chances of developing baldness, and also in those with hair thinness and weakness.
PRP is administered in Arogyam Hair Transplant and Cosmetic Clinic. The latest techniques are used for PRP and imported vials and reagents are used. The whole process takes 1 hour. Prior booking has to be done for the procedure. Please call at 7637089211/8811077011 for further details and to book an appointment.
PRP in Arogyam is done using the latest technology of needless injector. This is a special device where there is no needle and instead the solution is injected into the scalp at high pressure producing a painless PRP.
You can read up more on PRP in male pattern baldness in these studies:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4622412/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4134641/
https://www.karger.com/Article/FullText/477671

Dr. P. J. Mazumdar is the only ABHRS
(American Board of Hair Restoration Surgery) Certified Diplomate in the NE. American Board Certification is achieved through a long process requiring evidence of excellent results and skilled experience, and passing a tough oral and theoretical examination. It ensures adherence to international norms of the ISHRS and ABHRS.
Best Hair Transplant Clinic in the North East Award
Arogyam Hair Transplant and Cosmetic Surgery Clinic is proud to announce that it has been awarded the "Best Hair Transplant Clinic in the North East" in the Iconic Awards 2018 by BRW in association with Times Now News channel.
Read More.jpg)

.jpg)
Arogyam Hair Transplant and Cosmetic Surgery Clinic is proud to announce that we were awarded the "Best Wellness Clinic in North East" by News 18 HealthCare Excellence Awards by Health Minister.
Read More"WHEN HOPE MEETS HAIR."
The staff and surgeon were very friendly, professional and responsive to my needs. Excellent results.
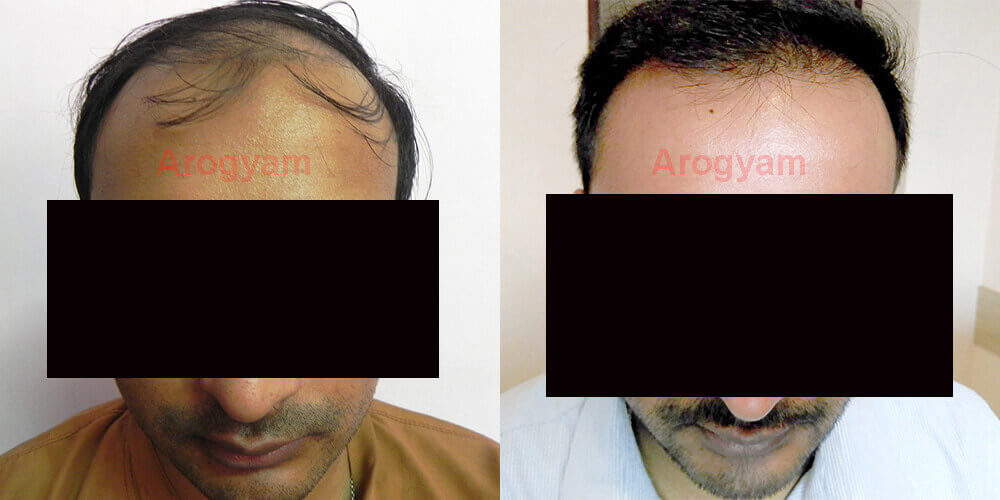
The best clinic in North East. They are 1st Hair transplant clinic in North East.

The experience was awesome with your treatment... So happy with the great results, I am very satisfied
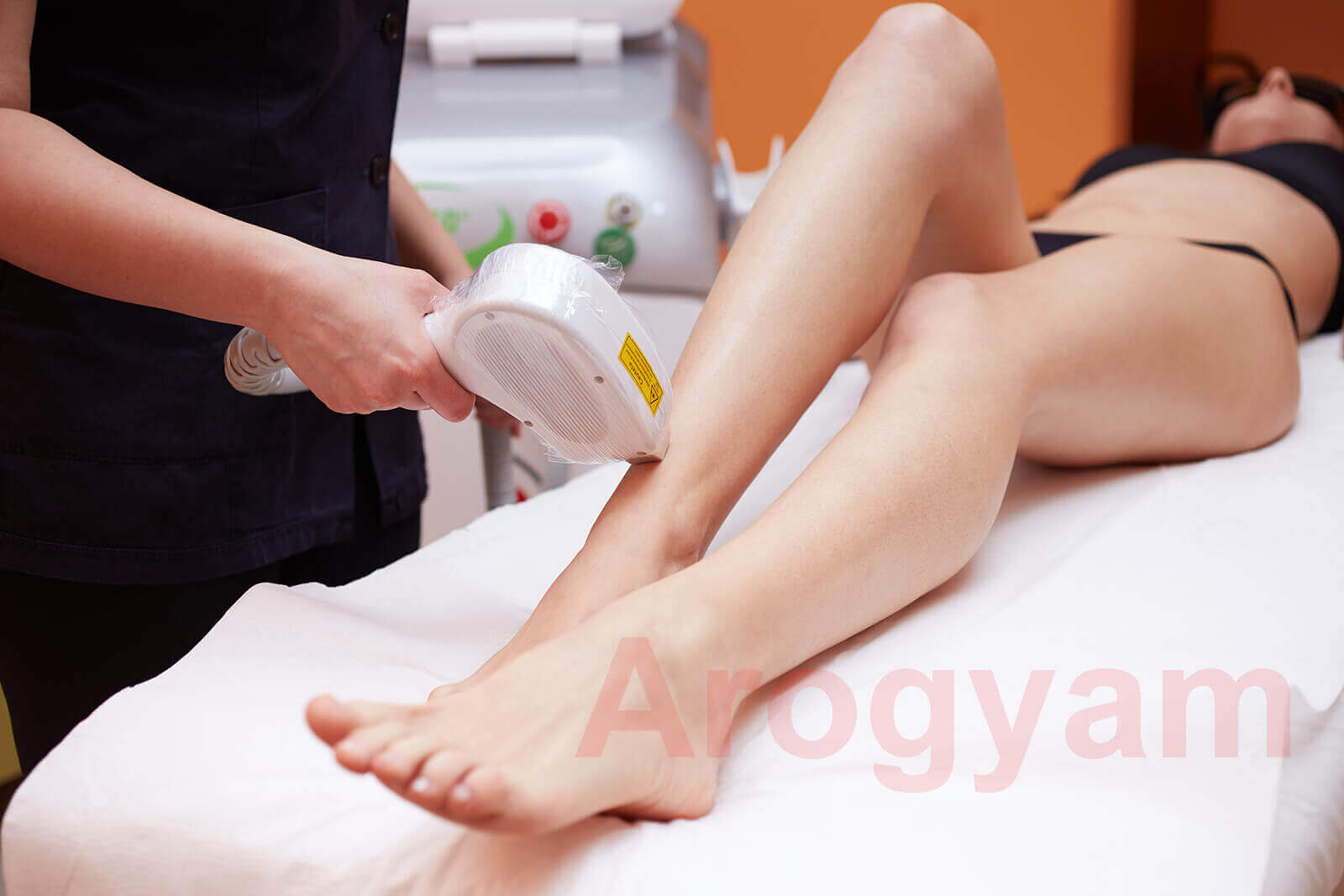


Laser hair removal is used to remove unwanted hair from the body permanently. Arogyam Hair Transplant and Cosmetic Surgery Clinic uses the best and most advanced laser, the Diode laser with 808nm frequency, in combination with IPL for Dual Laser hair removal in Guwahati.
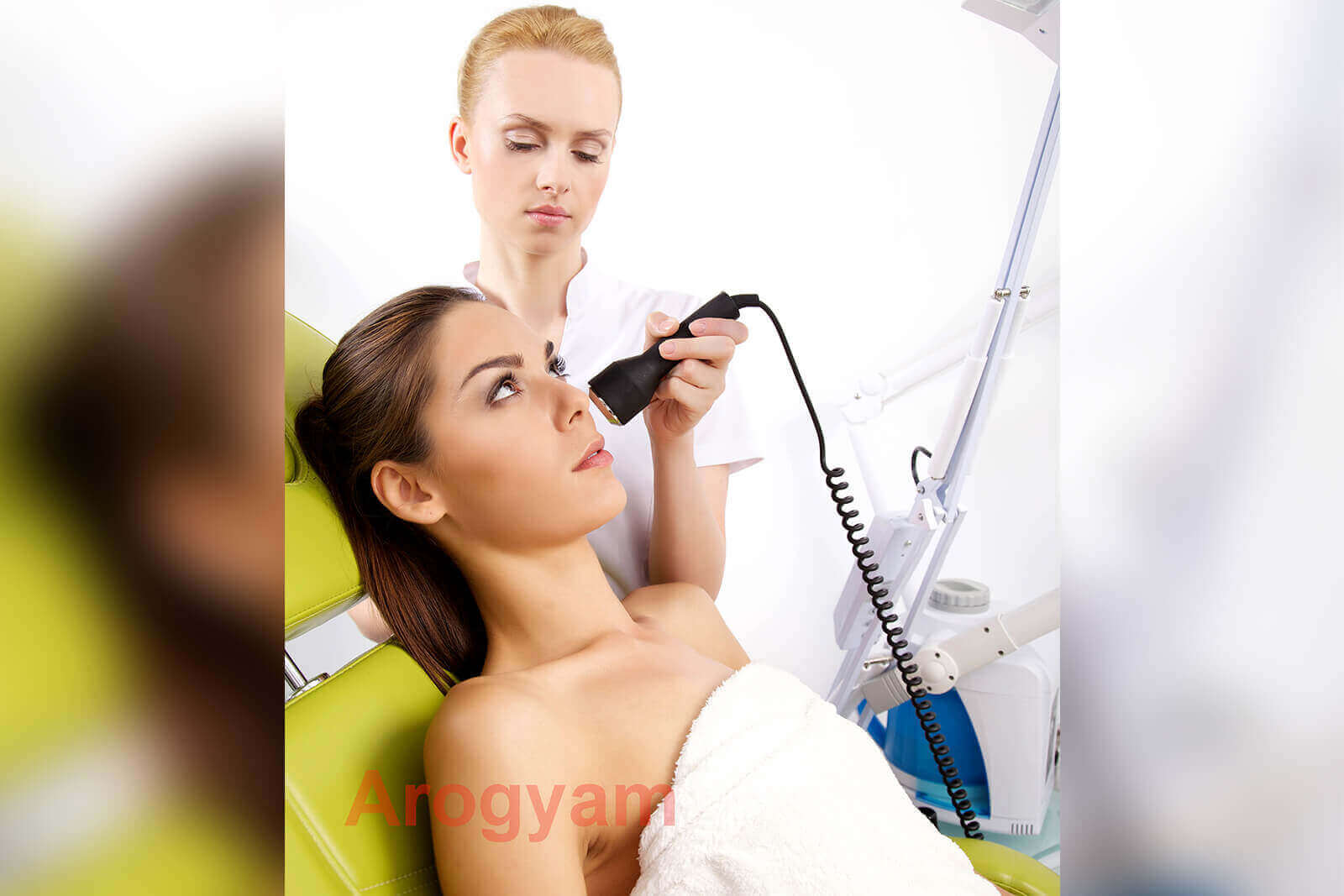
Arogyam Hair Transplant and Cosmetic Surgery Clinic has a highly advanced platform containing IPL, RF and Nd-Yag Laser, which are all different forms of energy treatment of skin. These different types of energy treatments are complementary to each other and they help the skin in different ways so that a combination works better than any individual treatment. For example, a combination of IPL acne treatment plus Nd Yag black doll facial treatment works in different ways on acne and help to cure it faster.
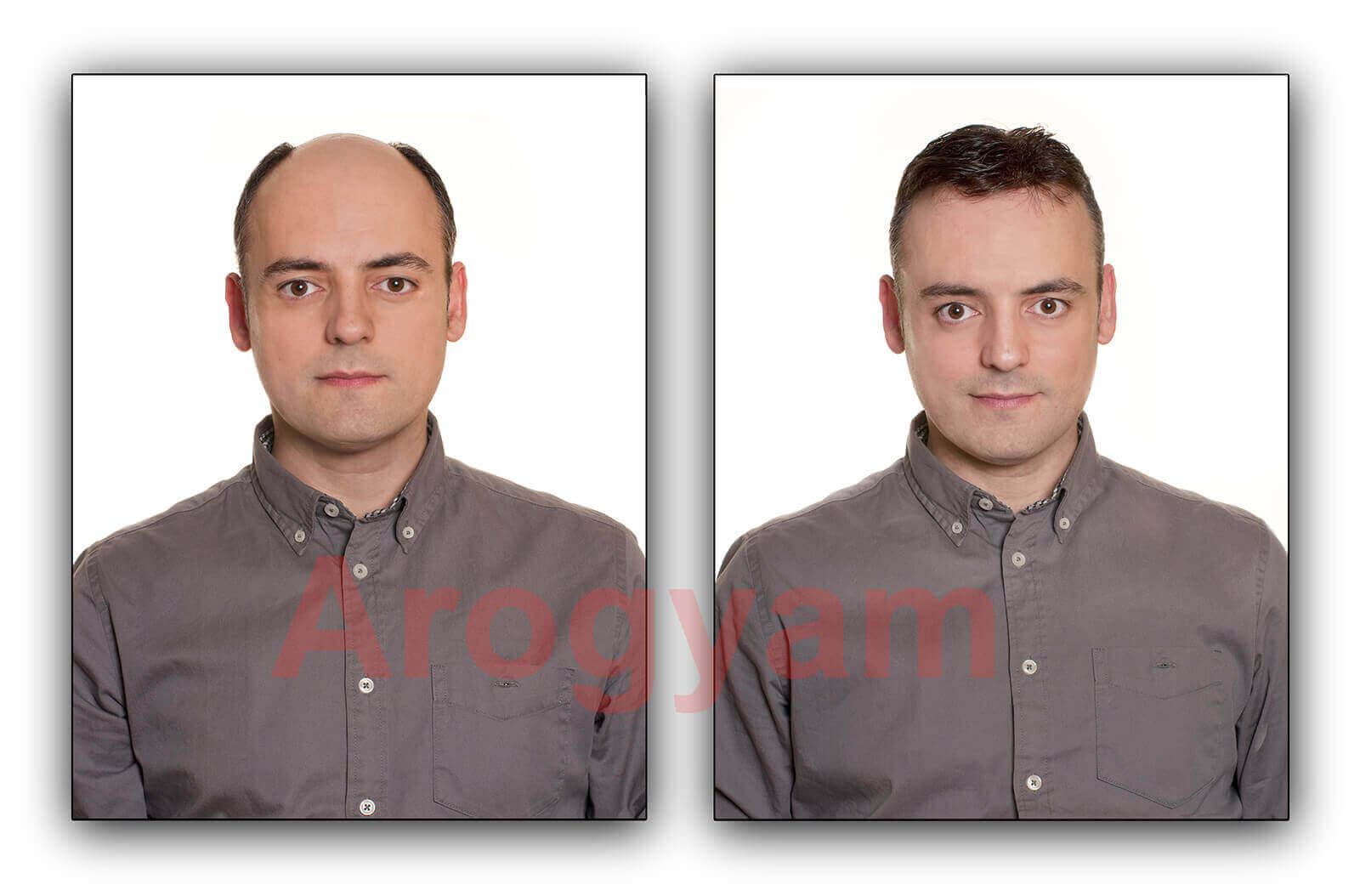


Hair patch or wig is a fast and convenient non surgical treatment for baldness and hair loss. Arogyam Hair Transplant and Cosmetic Surgery Clinic, Guwahati, provides customized hair patches which are specially created to fit the customer's head very naturally. Our hair patches are also of a very high quality and are made of human hair with special skin coloured mesh.
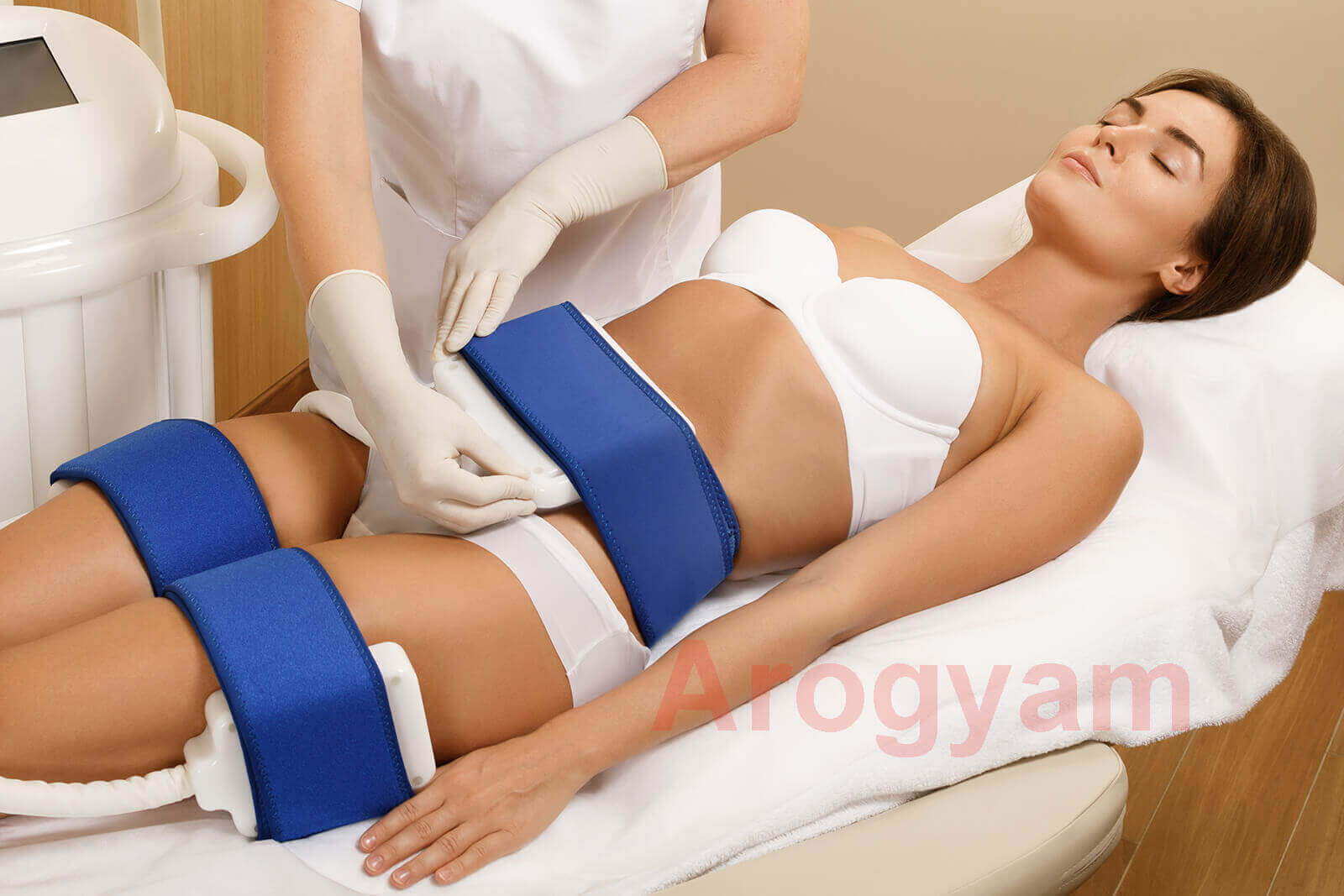
Cryolipolysis or CoolSculpting is a non invasive process in which localized fat bulges such as those in the stomach, arms, thighs, etc are treated by freezing the fat cells so that they can be removed easily and painlessly

Please leave a Google Review
if you have enjoyed our services
Arogyam Hair Transplant Clinic takes several steps to ensure that quality is maintained for each and every patient. The key to quality maintenance is to implement quantizable quality standards and maintain proper documentation and review of processes. Downtown Hospital is an ISO 9001:2008 and NABH accredited hospital which demands strict adherence to quality control.Steps taken are:
Safety assurance: all procedures are done in the main OT of Downtown Hospital with its full complement of anesthesiologists and critical care specialists. Hence patients are assured of full safety standards at the same level as that of major surgeries including transplant surgeries.
Sterilization assurance: since procedures are done in the major OT full sterilization is maintained. Fumigation is done every week and swab tests are done to check for contamination.
Best instrumentation: Arogyam Hair Transplant Clinic uses the best available instruments like 6X Heine Loupe for precision and accuracy, Blunt Titanium punches which avoids damage and transection of the Follicular Units, Choi implanters to standardise the process of planting and prevent damage during planting, Major OT level sterilization, fumigation and autoclaving of all instruments, etc.
Efficiency count: Efficiency counts for FUE like transection rates and speed of transplant are noted and documented for each case and reviewed every 10 cases. Arogyam Hair Transplant achieves international standards of transection and speed consistently.
Counting trays: Counting trays are used to contain the follicular units and all patients are given photographs on their mobiles which they can use to easily count the number of follicular units taken out so that they can be sure that they have received the correct number of FU's.
Dr. P. J. Mazumdar is the first and only American Board Certified Diplomate of the American Board of Hair Restoration Surgery and all procedures are done following the ethical and technical guidelines of the American Board of Hair Restoration Surgery and the International Society for Hair Restoration Surgery. As such, patients can be assured of receiving full professional care as per International standards approved by the ABHRS and ISHRS.
Correct recepient density: To ensure correct recepient density, 'density stamps' are used to ensure proper density is achieved. Angle and direction of hair is meticulously maintained.
Out of body time: The out of body time, the time for which the follicular unit is outside the body, is the most critical factor for success in hair transplant. Aroyam Hair Transplant follows a special procedure to ensure that this time is the minimum. This is done by doing only 1000 follicular units at a time and then replanting them. This ensures that time out of body is less than or equal to1 hour only. This is the shortest period acheivable. Many centers do upto 2000-2500 follicular units at a time so that time out of body goes upto 4-5 hours. We are proud of our time out of body quantum. Though this may cause some sacrifice of time but results are more important.
Follow up: follow up period is critical for the patient when there are many doubts and anxieties in his mind. In our clinic, Dr. P. J. Mazumdar will remain always accessible to the patient directly on his personal mobile for any questions the patient may have during this period.
নিবন্ধের তালিকা
Disclaimer: Results can vary from person to person. Hair Transplant is a surgical procedure and consists only of removing hair from hair growing regions and restoring it to hair deficient regions.
Privacy Policy: We use only the information submitted by you through the contact form. We do not share this data with any third party. We use Google Analytics to analyse the log data. For full privacy policy, read up here.
The academic certificates of Dr. P. J. Mazumdar may be examined here: Academic Certificates. His resume can be perused here: Resume. To find the contact address and other details, go to Contact. The blog contains various blog posts mainly on Hair Transplant. To see photos of hair transplant cases done in Downtown Hair transplant clinic, go to Photos>Results from the Navigation menu. To see videos related to Hair Transplant Procedure, go to Photos>Videos from the Navigation menu.
